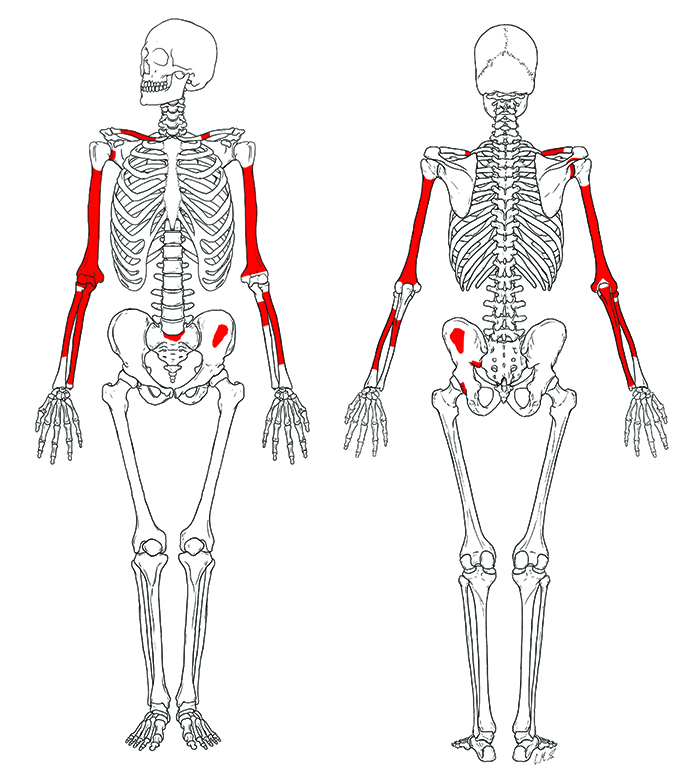
The new, exceptionally complete Homo habilis skeleton (specimen KNM-ER 64061) found in the Lake Turkana Basin of Kenya is dated to between 2.02 and 2.06 million years old. Discovered in the Koobi Fora Formation, this 2026-analyzed find provides the most complete postcranial remains of the species ever found, showing unexpectedly primitive, long arms https://www.sciencealert.com/this-2-million-year-old-fossil-may-be-the-oldest-example-of-an-early-human
So far, only two cranial sections with associated dental remains have been found for Homo erectus and three for Homo habilis. Recent compelling evidence suggests that both species co-existed in eastern Africa between 2.2 and 1.8 million years ago. Plus, several other hominin species probably lived at this time and in the same region: P. boisei and H. rudolfensis.

we could not reject the hypothesis that A. sediba shares its closest phylogenetic affinities with the genus Homo. Therefore, based on currently available craniodental evidence, we conclude that A. sediba is plausibly the terminal end of a lineage that shared a common ancestor with the earliest representatives of Homo.
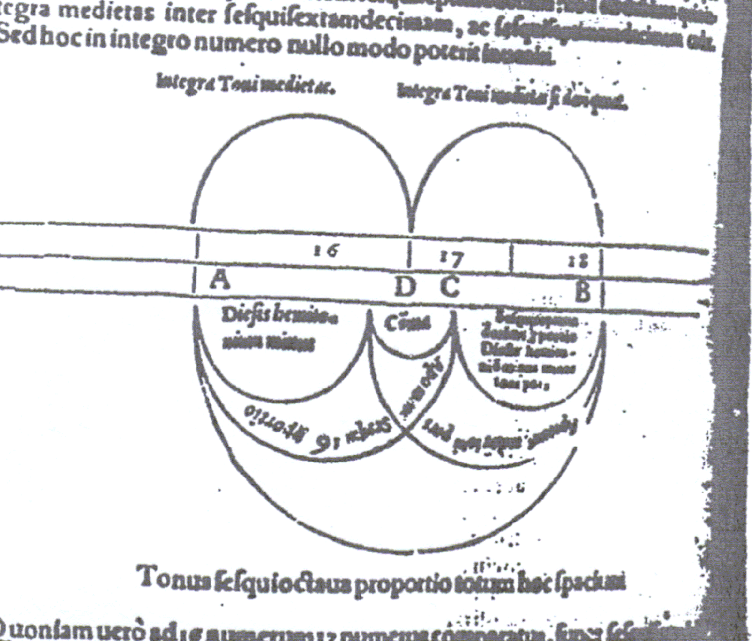
A. Sediba 2 million year old ancestor of Homo?
We report the presence of Homo at 2.78 and 2.59 million years ago and Australopithecus at 2.63 million years ago. Although the Australopithecus specimens cannot yet be identified to species level, their morphology differs from A. afarensis and Australopithecus garhi. These specimens suggest that Australopithecus and early Homo co-existed as two non-robust lineages in the Afar Region before 2.5 million years ago, and that the hominin fossil record is more diverse than previously known. Accordingly, there were as many as four hominin lineages living in eastern Africa between 3.0 and 2.5 million years ago: early Homo1, Paranthropus2, A. garhi3, and the newly discovered Ledi-Geraru Australopithecus.
3.4 million year old Hominin? vid
Australopithecus is a genus of early, bipedal hominins that lived in Africa approximately 4.18 to 2 million years ago. As direct ancestors or close relatives to the Homo genus, they are characterized by a mix of ape-like features (small brains, 400–500 cc) and human-like traits, such as bipedalism
An opposable big toe like a thumb - to grasp trees
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zIZSyPMoHIU
Australopithecus used and made stone tools just like Homo habilis....
No comments:
Post a Comment