Several studies have highlighted the health benefits of low‐to‐moderate drinking in reducing the risks of cardiovascular disease (Di Castelnuovo et al., 2017; Fernando, 2017; Minzer et al., 2020; Shah et al., 2018). However, other studies suggest that even low‐to‐moderate alcohol intake might still pose some risk (Charlet & Heinz, 2017; O'Keefe et al., 2018; Wilson & Braillon, 2018).
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10494618/
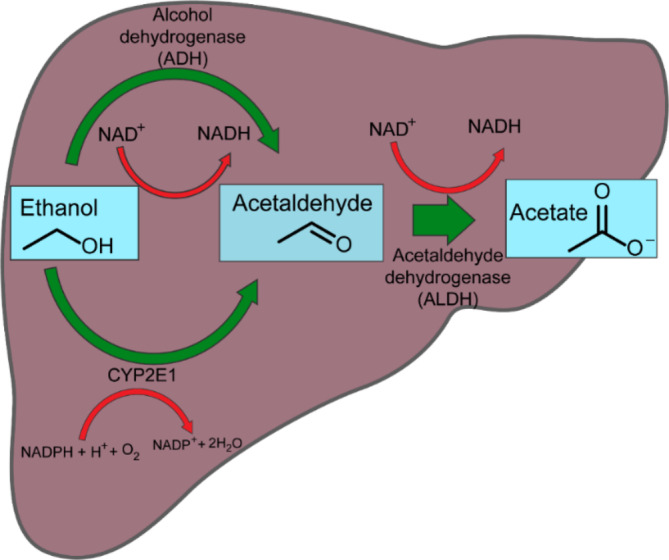
There are two main pathways that enable metabolization of ethanol: alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and cytochrome P4502E1 (CYP2E1). ADH catalyzes the oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde, which is further oxidized to acetate by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) (Figure 2). In addition, catalase oxidation in the third pathway especially in the brain and when oxidative stress develops (Jiang et al., 2020; Wilson & Matschinsky, 2020).
In total, we found 43 terpenoids used in the treatment of NAFLD. Over a dozen terpenoid compounds of natural origin were classified into five categories according to their structure: monoterpenoids, sesquiterpenoids, diterpenoids, triterpenoids, and tetraterpenoids. We found that terpenoids play a therapeutic role in NAFLD, mainly by regulating lipid metabolism disorder, insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammation. The AMPK, PPARs, Nrf-2, and SIRT 1 pathways are the main targets for terpenoid treatment.
Alcohol produces DNA mutations primarily by breaking down into acetaldehyde, a toxic byproduct that causes direct damage, such as interstrand crosslinks (ICLs) and double-strand breaks.
best natural food source of glutathione...The best natural, direct food sources of glutathione are fresh, uncooked vegetables like asparagus, avocado, spinach, and okra.
Acetaldehyde, a highly reactive and toxic substance generated during alcohol metabolism, primarily causes DNA mutations, chromosomal damage, structural and functional impairments of organ, and the development of tumors by forming various adducts with DNA and proteins
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12031026/
human ADH is classified into five types, with classes I, II, and IV being involved primarily in ethanol metabolism under physiological conditions...Class IV ADH was recently detected in the esophagus and stomach and was found to be responsible primarily for first-pass ethanol clearance. 27 Approximately one-third of Asian individuals do not express it....
Low ALDH1A1 activity is associated with a mild alcohol flush reaction in European individuals but has little impact on drinking behavior.
A genetic variant, ALDH2*2 (rs671), prevalent in East Asian populations, disrupts the ALDH2 tetramer and significantly reduces its ability to metabolize acetaldehyde. 33 34 Carriers experience discomfort (e.g., nausea and headache) after ethanol intake, which reduces their risk of AUD and acute alcohol-related disease development.
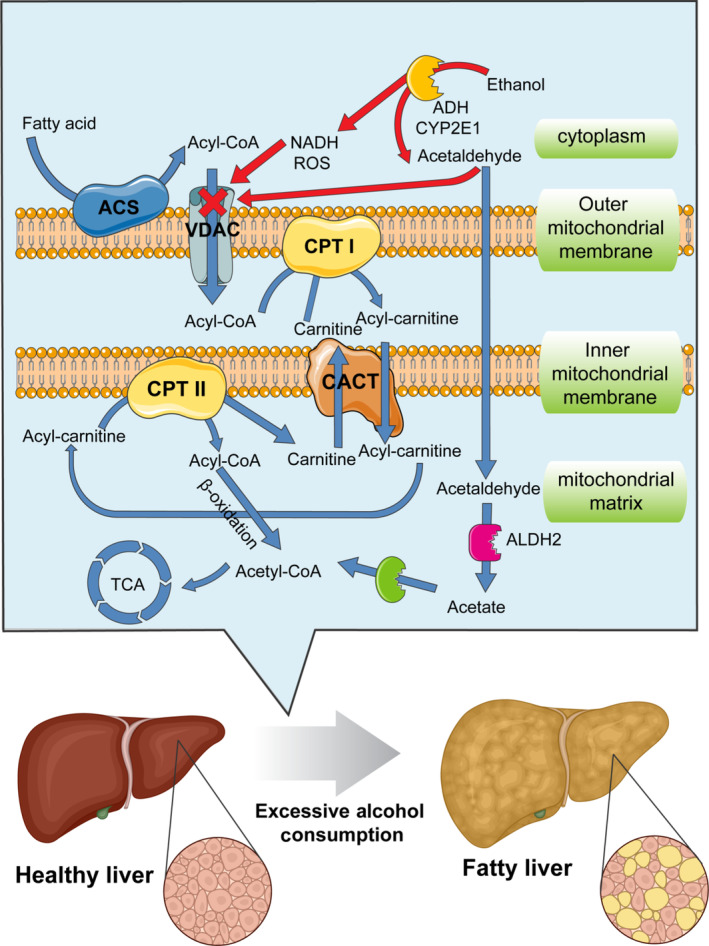
Chronic alcohol consumption can induce the expression of CYP2E1, which may be associated with faster alcohol clearance in heavy drinkers. CYP2E1 is also involved in the oxidation of compounds such as benzene and acetone, and it exacerbates oxidative stress in hepatocytes by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). 39
CAT [catalase] plays an important role in alcohol metabolism in the brain, and its metabolite acetaldehyde is considered to be a key factor in alcohol reinforcing effects, tolerance, and voluntary ethanol intake. These effects are likely related closely to the interaction of acetaldehyde with catecholamines to produce various condensation products
Natural food sources of catalase includeraw fruits, vegetables, and organ meats, with particularly high concentrations found in broccoli, spinach, kale, onions, potatoes, and root vegetables. Fruits like bananas, pineapples, and cherries, along with raw dairy and liver, are excellent sources to help reduce oxidative stress
Mechanistically, alcohol-induced CYP2E1 overexpression enhances HBV replication by upregulating hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α, the key transcription factor for the HBV core promoter, 117 and increases HCV-related mitochondrial ROS, reducing antioxidant capacity and depleting mitochondrial glutathione, which heightens oxidative damage and cell death. 118 However, both ethanol (via CYP2E1) and HBV can induce oxidative stress, complicating differentiation of their roles in liver damage.
MASLD (formerly known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [NAFLD]) has become the most common cause of CLD worldwide....According to a recent meta-analysis, the global prevalence of MASLD has surpassed 30% and continues to increase
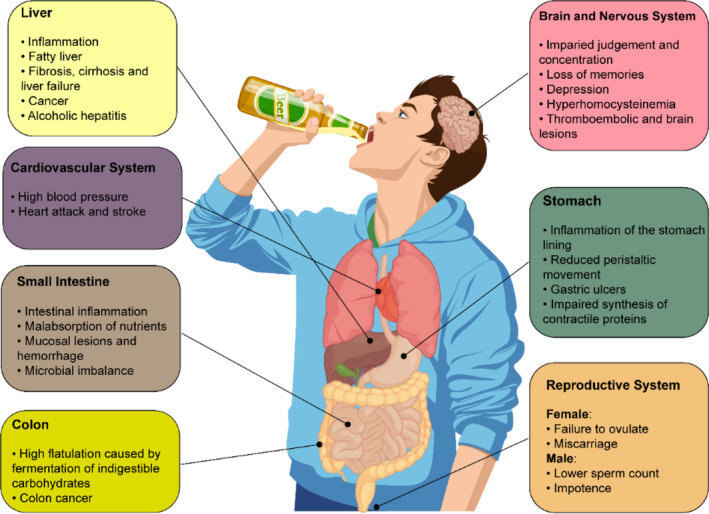
Alcohol causes fatty liver (hepatic steatosis) by overwhelming the liver's ability to process toxins, leading to fat buildup from increased production and decreased breakdown of fatty acids, plus reduced fat export, disrupting normal lipid metabolism through various molecular pathways that promote fat synthesis and hinder oxidation, often starting with shifts in the NADH/NAD+ balance and involving inflammatory signals like TNF-α
The metabolism of alcohol creates a large amount of NADH, which inhibits the liver's ability to burn fat (fatty acid oxidation).
increases the production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α),
Your liver breaks down alcohol, but heavy drinking produces harmful byproducts (like acetaldehyde) and puts stress on liver cells, interfering with its normal functions, including fat processing.
Alcohol metabolism shifts the liver's balance (increasing NADH), promoting the creation of glycerol-3-phosphate, which combines with fatty acids to form triglycerides (fat). It also activates SREBP-1c, boosting enzymes for fatty acid synthesis.
Chronic alcohol consumption not only reduces the NAD +/NADH ratio....NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) isa coenzyme used in therapy to assist alcohol recovery by replenishing levels depleted by chronic alcohol abuse. It is administered via IV to potentially reduce withdrawal symptoms, curb cravings, and aid in cellular energy production, though it is not a cure and studies are limited....
NAD+ and glutathione (GSH) are complementary, synergistic molecules that drive a "circular economy" for cellular health, acting as a powerful duo for energy, detoxification, and anti-aging.NAD+ acts as cellular fuel and helps regenerate glutathione, while glutathione reduces oxidative stress to protect NAD+
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) cannot be consumed directly through food, but you can boost its levels by eating foods rich in precursors like tryptophan, vitamin(niacin), and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR). Key dietary sources include fatty fish (salmon, tuna), poultry (turkey, chicken), dairy, eggs, peanuts, mushrooms, and green vegetables
From ages 20 to 60, NAD+ drops by 50%, while glutathione synthesis decreases by 45%
Alcohol, once consumed, suppresses the appetite in the alcoholics by elevating the secretion of tumor necrosis factor‐α (TNF‐α) and leptin (the satiety hormone secreted by adipose tissues). This is followed by upregulation of the secondary inflammatory factors including interleukin‐1β (IL‐1β), interleukin‐6 (IL‐6), and interleukin‐8 (IL‐8) by TNF‐α, which further suppresses appetite (Kamran et al., 2020). Followed by diarrhea induced by ethanol, the lower sodium concertation leads to reduced activity of sodium–potassium ATPase and glutathione/glucose cotransporters on the intestinal cell surface (Butts et al., 2019). Moreover, excessive alcohol prevents protein synthesis in the small intestine: Contractile proteins are less likely to be synthesized in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract of alcohol drinkers in which peristaltic movements and transition time of food are adversely affected (Thomson et al., 2017). These malnutrition and malabsorption are exacerbated in the drinkers when metabolism of essential nutrients is affected. For example, folate is an important vitamin for the development of fetal nervous system and its absorption is largely affected by alcohol consumption....
Considering the high prevalence of malnutrition and malabsorption in heavy drinkers of alcohol, their bodies often suffer from the depletion of carnitine and other micronutrients such as lysine and methionine (precursors of carnitine). Given the crucial role of carnitine in facilitating fatty acid metabolism, its reduced levels can significantly affect hepatic fatty acid beta‐oxidation in alcoholics.
alcohol is consumed along with the food, it contributes to the formation of free radicals and the activation of pro‐carcinogens by induction of CYP2E1. Ethanol can serve as a solvent to dissolve the carcinogens that are considered a contributing risk factor in promoting esophageal cancer and facilitating their penetration into the aerodigestive mucosa (Alzeer & Abou Hadeed, 2016; Husain et al., 2011). Acetaldehyde and other generated aldehydes during oxidative stress can cross‐react to form hybrid adducts composed of different combinations of acetaldehyde‐protein or acetaldehyde‐DNA in the tissues. The clinical significance of this phenomenon is accelerated when alcohol is consumed with high levels of fat (which is susceptible to oxidative conditions) or iron‐enriched food (which acts as a pro‐oxidant) (Hyun et al., 2021; Niemela, 2001). However, one potential treatment can be the use of dietary bioactive agents to eliminate or minimize the development of next‐day hangover symptoms
A liquid‐based formula named Oh!K, composed of ginger, green tea, turmeric, and pepper, could successfully diminish post‐alcohol disorders in intoxicated drinkers (Sreeraj Gopi et al., 2014).
this translates to about 13 mg of glutathione per 100 grams of fresh spinach.
Dandelion juice could increase the concentrations of plasma ALDH and expression of catalase and glutathione reductase in males aged 24–28 years
As a result of the fermentation process, fruit meads lost from 3.5% of total polyphenols with Cornelian cherry juice from the fruit of the ‘Podolski’ (PF) cultivar to 10% with juice from the fruit of the ‘Koralovyi’ cultivar (KF). Aging reduced polyphenols in the final products from 22% in the mead with juice from the fruit of the ‘Podolski’ cultivar (PA) to 53% in the mead with juice from fruit of the ‘Jantarnyi’ cultivar (JA). The entire technological process decreased the content of polyphenols in fruit meads from 25% in the PA sample to 56% in the JA sample.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8394733/
Fermented beverages based on raw materials with a high content of polyphenols can be a very good source of natural antioxidants, because the drinks are directly absorbed into intestinal fluids, thanks to which their digestibility by the body is higher than that of food products [21].
a result of the alcoholic fermentation of honey Cornelian cherry wort, decreased from 2% in variants with yellow fruit juice (JF) to 14.5% in variants with red fruit juice (PA). The aging stage also reduced the content of identified iridoids in the final products, from 4% in JA mead to 12% in KA mead. Iridoids are a distinct class of secondary metabolites (specifically, oxygenated monoterpenoids).
In this context, NADH acts as a reducing agent (electron donor), becoming oxidized to
In this context, NADH acts as a reducing agent (electron donor), becoming oxidized to
In this context, NADH acts as a reducing agent (electron donor), becoming oxidized towhile reducing the iridoid substrate
Cornelian cherry juice comes from Cornus mas (a dogwood tree fruit),
the Cornelian cherry dogwood (Cornus mas)
Saffron Sentinel® Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas 'JFS PN4Legacy') is a columnar, deciduous tree, approximately 22 feet tall and 12 feet wide,
Cranberries are also a good source of iridoid
The earliest record of mead was discovered in pottery from Henan province in northern China, dating back to around 9000 BCE. This pottery contained a fermented mixture of honey and wild grapes. Mead was also known as ‘drinkable honey’, ‘wedding wine’ or ‘love drink’. The term ‘honeymoon’ was coined due to the tradition of newlyweds drinking mead for a month after the ceremony to pray for their unborn children (Gangl et al., 2018; A. P. Pereira et al., 2017). In literature, mead was mentioned as a superior drink, such as in the Sag and Beowulf. In African markets, mead was even used as a medium of exchange (Katoh et al., 2011). In Asia, mead was considered the drink of the nobility and the gods. People believed that drinking mead could improve their spirit, wisdom and life (Balogu & Towobola, 2017).
No comments:
Post a Comment